
Cardiovascular Implications of ED
- Written

When we talk about men’s health, a few topics are uncomfortable to discuss. One of them is Erectile Dysfunction (ED). Because of its intimate nature, people talk about it in whispers or do not talk about it at all.
However, addressing ED as a health concern is crucial. According to the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, ED affects about 30 million men in the United States. Even though it’s so common, 75 percent of men don’t consult with doctors about available ED solutions.
The taboo and the social stigma prevent men from seeking medical help. However, erectile dysfunction is a serious concern, and it is vital to address it. On the surface, erectile dysfunction feels like just a bedroom issue. But it goes beyond its impact on intimacy.
According to research, erectile dysfunction is recognized as a potential indicator of one’s cardiovascular health. It can be an early warning sign of existing or future heart problems. ED and heart issues may sound unrelated, but they are closely intertwined as they share similar risk factors and mechanisms.
In this article, we dive into the overview of the basics of erectile dysfunction, its prevalence and cause, and most importantly, its ties to cardiovascular health. Let’s understand the connection between ED and your heart in the following sections -
Introduction to Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Understanding Erectile Dysfunction
The Connection Between Erectile Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Health
ED as a Potential Early Warning Sign of Cardiovascular Disease
Managing Erectile Dysfunction and Promoting Cardiovascular Health
Case Studies and Success Stories
ED and Heart Health: An Overview
I. Introduction to Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
A. Definition of Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Erectile Dysfunction (ED) is a medical condition in which one is unable to develop and maintain an erection for satisfactory sexual intercourse or activity. It can influence both one's physiological efficiency in achieving an erection and one's desire for sensations of arousal and desire for sexual desire.
While there are no uniform criteria for consistency and duration, ED can be both occasional and frequent. Infrequent erectile dysfunction is not necessarily a medical condition. Most men experience it due to stress, nutritional changes, lifestyle alterations, or other factors. However, frequent erectile dysfunction can be a sign of a disorder and needs treatment.
B. Prevalence and Demographics
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is a prevalent concern that can impact men of all ages. However, its prevalence increases as men age older.
The University of Wisconsin estimates that the prevalence of ED rises by 10% every decade of life for men. Moreover, The Massachusetts Male Aging Study, the most cited study by experts in discussions of prevalence, states ED increases from about 5 to 15 percent between ages 40 and 70. It is mostly because of physiological changes, such as reduced blood flow and hormone fluctuations.
However, young men can also experience ED. According to a study by the National Library of Medicine in the UK, out of 5,185, 29.3% of men aged between 18-30 had ED.
The same study also observed significant differences in demographic characteristics of men with and without ED. Have a look at the table.
C. The Link Between ED and Cardiovascular Health
In 2018, researchers conducted a study that strongly confirmed the ties between erectile dysfunction and cardiovascular risk. 1900 men aged between 60 and 78 took part in this four-year study. The results were shocking — it reported that men suffering from erectile dysfunction are twice as likely to suffer from a heart attack.
This is why erectile dysfunction has been declared an independent predictor of future cardiovascular events.
II. Understanding Erectile Dysfunction

A. Causes of ED
The possible causes of ED can include both physical and psychological factors. Let’s have a look at them -
Physical Factors
- Cardiovascular disease
- Diabetes
- Hypertension or high blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Obesity
- Low testosterone levels or other hormone imbalances
- Kidney issues
- Sleep disorders
- Drug use
- Excessive alcohol consumption
- Liver cirrhosis
- Epilepsy
- Excessive tobacco use
- Parkinson’s disease
- Multiple sclerosis
- Peyronie’s disease
Psychological Factors
- Stress
- Anxiety
- Depression
- Self-esteem issues
- Performance anxiety
- Relationship issues
B. Risk Factors for ED
A few factors can increase the risk of erectile dysfunction in men. Let’s see what they are -
1. Age
The risk of ED increases in men as they age. It is why ED is more common in older men than in younger men. While several factors dictate the severity of ED with age, it’s due to changes in blood flow, hormone levels, natural decline in sexual function, and overall health.
2. Lifestyle Choices
Excessive smoke and alcohol consumption damages blood vessels and impacts sexual function, leading to an increase in risk for ED. Moreover, if you follow a sedentary lifestyle with no regular physical activity, it counts as a risk factor for ED.
3. Chronic Conditions (diabetes, hypertension, etc.)
Conditions like diabetes, hypertension, obesity, and heart disease can affect the risks of developing ED.
III. The Connection Between Erectile Dysfunction and Cardiovascular Health
Here is a detailed explanation of the connection between erectile dysfunction and cardiovascular health -
A. Shared Risk Factors
There are common risk factors associated with ED and heart health. Here are a few of them -
1. Atherosclerosis
Atherosclerosis is the most common reason for ED. It is a medical condition where a buildup of plaque (fat and cholesterol) thickens the inner lining of an artery. It slows down or restricts the blood flow in your body, including the heart and the penis. The former enhances the risk of a heart attack, while the latter causes difficulty in obtaining and maintaining an erection.
2. Endothelial Dysfunction
Endothelial Dysfunction occurs when the large blood vessels on the heart's surface constrict (narrow) instead of dilating (opening). It impacts the blood supply to the heart and penis, contributing to heart issues and erectile dysfunction, respectively.
3. Inflammation
Chronic inflammation is an underlying cause of cardiovascular diseases and ED. In the case of erectile dysfunction, it can impact the ability to dilate and allow sufficient blood flow to the penile region. Additionally, it promotes the accumulation of plaque, increasing the risk of atherosclerosis and therefore, heart disease and ED.
B. Mechanisms Linking ED and Cardiovascular Disease
Let’s understand the key mechanisms that link ED and cardiovascular diseases -
1. Nitric Oxide Pathway
Nitric oxide, being a vasodilator, helps in the process of widening blood vessels. Aging, poor lifestyle habits, diabetes, or hypertension can reduce nitric oxide production. It can lead to a decrease in blood flow, leading to negative effects on both erectile function and cardiovascular health.
2. Vascular Health and Blood Flow
The overall well-being of your blood vessels, including arteries, veins, and capillaries, defines your vascular health. However, when blood vessels get clogged due to fatty buildup, blood flow slows down. It leads to difficulties in getting an erection and causes heart problems.
3. Role of Hormones
Testosterone is the primary male sex hormone responsible for regulating sexual desire (libido) and erectile function. Its low levels can reduce nitric oxide production, affecting not just erection but also heart health.
IV. ED as a Potential Early Warning Sign of Cardiovascular Disease

A. Importance of Early Detection and Intervention
Now that we know erectile dysfunction is not an isolated concern and shares risk factors with cardiovascular disease, it’s vital to intervene in the early stages to prevent potential heart issues. You see, ED symptoms can show up before symptoms of heart disease. It’s because blood vessels in the penile region are smaller than those in other parts of the body. So, if you detect ED and take the needed treatment, it can reduce the risk of developing heart problems.
B. Role of Healthcare Providers in Recognizing the Connection
Healthcare providers need to adopt a proactive role while diagnosing and treating ED to evaluate potential cardiovascular issues in a patient. Both ED and cardiovascular diseases have common risk factors. Therefore, when a patient is diagnosed with ED, medical professionals should run tests and perform checkups to analyze the risk of current or future heart problems. If a risk persists, they can take immediate action to help patients mitigate it.
C. Screening and Diagnostic Approaches
Healthcare professionals should perform screenings to assess blood pressure, cholesterol levels, blood glucose, and lifestyle habits. If the results show mild or serious risk, further diagnostic tests, such as stress tests and coronary angiography, are required to evaluate the heart’s health.
V. Managing Erectile Dysfunction and Promoting Cardiovascular Health

Effective management of ED and heart health requires a holistic approach towards well-being. It includes lifestyle modifications, treatments for ED, and cardiovascular disease management.
A. Lifestyle Modifications
1. Diet and Exercise Recommendations
If you incorporate a healthy diet and regular exercise into your lifestyle, you can promote proper blood circulation, improving both ED and heart health. Follow a diet routine with several fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats. A study by the National Library of Medicine states that the Mediterranean diet also contributes to preserving sexual function. Moreover, foods rich in flavonoids, such as cocoa and dark chocolate, tea, and wine, reduce the risk of ED.
Regular exercise can also help with ED and cardiovascular health. Several studies suggest kegel, aerobic, yoga, and pelvic floor muscle exercises significantly improve penile function.
2. Smoking Cessation
The nicotine in cigarettes constricts blood vessels, reducing blood flow. It directly impacts both ED and heart health. If you quit smoking, you can significantly improve blood vessel health, which would help with both conditions.
3. Stress Management
Chronic stress and anxiety release such hormones that constrict your blood vessels. Seek stress management techniques to promote relaxation and reduce stress levels. It can include therapy, meditation, yoga, acupuncture, and deep breathing exercises.
B. Treatments for ED
1. Oral Medications (PDE5 inhibitors)
When you consult a doctor for ED, they may prescribe you meditation. The most common oral medications are Phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors that enhance the effect of nitric oxide in your body. Here are a few of them -
- Avanafil (Stendra)
- Sildenafil (Viagra)
- Tadalafil (Cialis)
- Vardenafil (Levitra, Staxyn)
2. Hormone Therapy
If you have low testosterone levels, your doctor can recommend Testosterone Replacement Therapy (TRT) to improve both sexual function and heart health.
3. Vacuum Erection Devices and Implants
If you don’t respond to other treatments, non-invasive vacuum erection devices are recommended. They draw blood into the penis and create an erection. One of the best products in the market is a penis pump that can increase the girth and length of your penis. Available in various sizes, it applies a pressure of 0 to 50 KPA to give the best penis enlargement results.
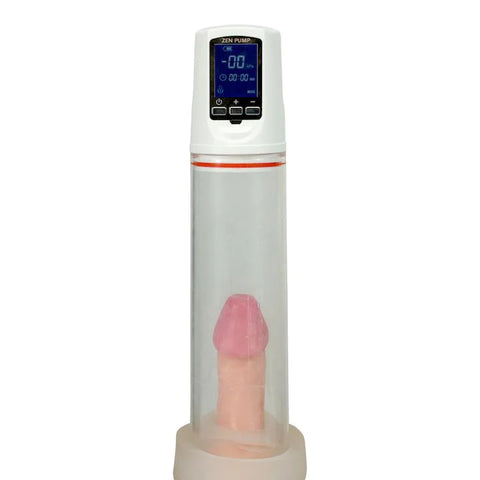
You can also opt for a penile implant as an effective ED treatment. An inflatable implant can make your penis larger, while a malleable implant manually adjusts the penis’ position.
C. Cardiovascular Disease Management
1. Medications
Several medications, including blood pressure medications, cholesterol-lowering drugs, and antiplatelet agents, can help in cardiovascular disease management, depending on the condition. Here are a few of them -
- Anticoagulants
- Antiplatelet therapies
- Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitors
- Angiotensin II receptor blockers
- Angiotensin receptor neprilysin inhibitors
- Beta-blockers
- Calcium channel blockers
- Cholesterol-lowering medications
- Digitalis
- Diuretics
- Vasodilators
2. Procedures
Procedures like angioplasty and stent placement are necessary in cases where arteries are significantly blocked. Other surgeries include valve replacement, repair surgery, device implantation (pacemakers and balloon catheters), laser treatment, and maze surgery.
3. Rehabilitation Programs
Cardiac rehabilitation programs can help you build heart-healthy habits. It includes supervised and regular physical activity, education on healthy living and eating, medicine prescriptions, and counseling to relieve stress.
VI. Case Studies and Success Stories
Real-life Examples of Individuals Benefiting From Addressing ED and Cardiovascular Health
If you’re suffering from ED and looking for a treatment that addresses your penile function, try an automatic penis pump by Zen Hanger.
Meet Bill, a middle-aged man who had been looking for a solution to improve his penile function and sexual life but couldn’t get satisfactory results. He heard of the penis pump on a discussion forum and tried an XL-sized pump. According to him, he used the pump twice a day for 15-minute sessions — once in the morning and then in the evening — for a month. To his surprise, he and his partner noticed a tangible change in his penis in just thirty days. He reports a gain of half an inch of girth and half an inch in length. It not only improved his sexual life but also boosted his self-confidence.
Bill’s success story is a testament that innovative solutions like the automatic penis pump can help you improve your sexual health.
VII. Conclusion
A. Recapitulation of the ED-Cardiovascular Link
Several studies and research have made it clear that ED and cardiovascular functions are interrelated. The shared risk factors and commonly linked mechanisms highlight the close relationship between the heart and sexual organs. Therefore, it is vital to adopt a holistic approach to manage these conditions and achieve overall well-being.
B. Importance of Seeking Professional Medical Advice
Every individual has a unique health history and journey. Generalized guidance cannot give effective results. Therefore, it is vital to consult healthcare experts, urologists, and cardiologists to get personalized treatment and lifestyle alteration advice.
C. Encouragement for Early Intervention and Lifestyle Changes
Now that we know the interlink between ED and cardiovascular health, we must leverage it to control and prevent its cardiovascular implications. Early intervention and lifestyle modifications can effectively prevent the development of underlying cardiovascular health issues.
Also, do not hesitate to try different treatment options to improve your penile health. At Zen Hanger, we offer all kinds of penis enlargement products to increase the girth and length of your penis. Visit our website and explore the product range to make an informed decision.
| Medical Disclaimer: If you have any medical conditions, questions, or concerns, please speak with your healthcare provider directly. The articles on Zen Hanger are underpinned by peer-reviewed research and information drawn from medical societies and governmental agencies. However, they are not a substitute for professional medical advice diagnosis, or treatment. |

